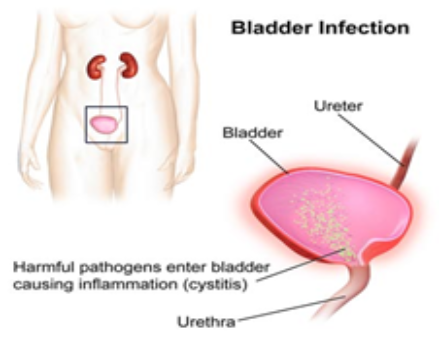

What Is a UTI?
A UTI is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections usually start in the lower urinary tract, where the urethra and bladder are located. The urethra is the tube that allows urine to pass out of your body. A UTI sometimes travels to the ureters and kidneys. The ureters are the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys (where urine is produced) to the bladder.1
Anyone can get a UTI, but these infections are most common in females or people with uteruses. The urethra is shorter and closer to the anus in females than in males.It's easier for bacteria to enter the body and ascend the urinary tract.
Symptoms
UTI symptoms typically include:
• Bloody, cloudy urine that might smell foul
• Frequency of urination
• Low-grade fever
• Lower abdomen or back cramps
• A strong urge to urinate
• Pain or burning when urinating
Severe symptoms can develop if a UTI travels from the bladder to one or both kidneys. Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) causes symptoms like fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, and severe abdominal pain.1
1. Apply Heat
Heat can be an effective home remedy for UTI pain in adults and children. Place a heating pad or hot water bottle on your abdomen or back to ease discomfort.
2. Fasting
Fasting for 24 hrs with water and 48 hrs with fruits are the best medicine to Detox bacteria from body.
3. Consume Cranberry Supplements
Some people swear by cranberry to prevent UTIs, but research has been limited and mixed. Cranberries contain proanthocyanidins. These chemicals prevent bacteria from sticking to cells lining the urinary tract.3 Note that cranberry supplements do not treat UTIs.
Cranberry supplements may be more palatable than tart cranberry juice. Talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting any supplements. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) minimally regulates cranberry supplements, which may not be suitable for you. The effects can vary and depend on many variables, including dosage, frequency of use, and interactions with current medications.
Cranberry juice may increase your risk of bleeding if you take warfarin (a blood thinner). The acidity may also trigger symptoms in people with interstitial cystitis, which causes pain and a feeling of pressure around the bladder. Additionally, juice contains a lot of sugar, which can increase the risk of UTIs.5 Be sure to consult with your provider if you take warfarin and contract a UTI before adding cranberry juice to your diet.
4. Try Vitamin C
Some people take vitamin C, which contains ascorbic acid, to prevent UTIs. The idea is vitamin C increases the acidity of urine, which staves off bacteria. In a review published in 2016, however, researchers could not recommend vitamin C to prevent UTIs. The researchers only noted two studies that had conflicting results.
Adding vitamin C to your regimen likely will not hurt if you are already taking cranberry and D-mannose (a type of sugar). Many supplements for bladder health combine all of these ingredients. Just make sure to talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting any supplements.
5. Try D-Mannose
D-mannose is a simple sugar that sticks to the bacteria Escherichia coli to prevent UTIs. A review published in 2020 found that D-mannose may prevent bacteria from clinging to the bladder and causing infection.
More research is needed to determine the optimal doses and side effects. Talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting D-mannose.
6. Urinate Frequently
Peeing every four hours, even if you do not feel the urge to go, may flush out bacteria that cause UTIs.10 Holding your pee until a better time or place is available may not be a good idea. The longer you hold in urine, the more time you give bacteria to stick to the urinary tract and cause infection.
Copyright © Al Shifa Naturopathy Clinic
Developed by : Xeromile